Difference between revisions of "Distribution panel"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Power distribution]] | [[Category:Power distribution]] | ||
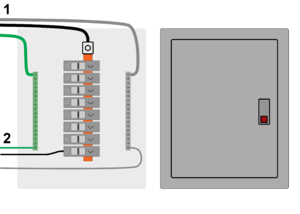
| − | [[File:Distributionpanel201105.png|thumb|right|Example of a distribution panel or load center:<br/> | + | [[File:Distributionpanel201105.png|thumb|right|'''Example of a distribution panel or load center:'''<br/> ''Left -'' Cover removed showing (1) Incoming L1, grounded conductor (neutral) and equipment ground from inverter. (2) Outgoing L1, grounded conductor (neutral) and equipment ground to loads.<br /> ''Right -'' Distribution panel with cover.]] |
In an off-grid PV system, the power coming from [[Types of electricity|alternating current (AC)]] and [[Types of electricity|direct current (DC)]] power sources that will be used to supply loads will typically pass through a distribution panel that will have [[Overcurrent protection|overcurrent protection devices]] that will allow small diameter wires to be run to outlets, lighting and other loads. There will also typically be [[Busbars|busbars]] for [[Grounding system|equipment grounding conductors]] and grounded conductors (AC neutral). A distribution panel may be a traditional distribution panel like is commonly seen in grid-connected electrical systems (as depicted in the graphic) or it may be a specifically designed for use in off-grid PV applications. They may differ in appearance, but the purpose and function is the same. A distribution panel must be suitable for the conditions in which it will be used including: | In an off-grid PV system, the power coming from [[Types of electricity|alternating current (AC)]] and [[Types of electricity|direct current (DC)]] power sources that will be used to supply loads will typically pass through a distribution panel that will have [[Overcurrent protection|overcurrent protection devices]] that will allow small diameter wires to be run to outlets, lighting and other loads. There will also typically be [[Busbars|busbars]] for [[Grounding system|equipment grounding conductors]] and grounded conductors (AC neutral). A distribution panel may be a traditional distribution panel like is commonly seen in grid-connected electrical systems (as depicted in the graphic) or it may be a specifically designed for use in off-grid PV applications. They may differ in appearance, but the purpose and function is the same. A distribution panel must be suitable for the conditions in which it will be used including: | ||
*Maximum ampacity | *Maximum ampacity | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 29 November 2020
In an off-grid PV system, the power coming from alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power sources that will be used to supply loads will typically pass through a distribution panel that will have overcurrent protection devices that will allow small diameter wires to be run to outlets, lighting and other loads. There will also typically be busbars for equipment grounding conductors and grounded conductors (AC neutral). A distribution panel may be a traditional distribution panel like is commonly seen in grid-connected electrical systems (as depicted in the graphic) or it may be a specifically designed for use in off-grid PV applications. They may differ in appearance, but the purpose and function is the same. A distribution panel must be suitable for the conditions in which it will be used including:
- Maximum ampacity
- Maximum voltage
- Phases (L1, L2, L3 etc.)
- Sufficient space for necessary overcurrent protection devices.
- Weather ratings
- Equipment certifications